MIG welding is a process that produces an electric arc between a wire electrode and the workpiece. MIG welding is an extremely versatile welding process that can be used to weld a variety of different metals.
In order to produce the best welds, it is important to set the correct polarity settings on your MIG welder.
In this blog post, we will discuss the different polarity settings and how to set them correctly for your specific project. Let’s get started!
MIG welding polarity
Polarity is simply the direction of the electrical current. In MIG welding, there are two types of polarity: direct current (DC) and alternating current (AC).
Each type of polarity has its own advantages and disadvantages.
Direct current (DC) is the most common type of polarity used in MIG welding. It produces a steadier arc than AC and is less likely to cause weld defects. DC is typically used for welding thick metals.
Alternating current (AC) produces a more erratic arc, but it is less likely to cause metal contamination. AC is typically used for welding thin metals.
Now that we know what polarity is, let’s discuss how to set it correctly on your MIG welder.
MIG welding polarity chart
MIG welding polarity is extremely important because it affects the way the welder transfers heat to the metal. If the welder uses the wrong polarity, they can either overheat or underheat the metal, which can lead to problems like warping, melting, or even explosions.
There are two types of MIG welding polarity- Straight Polarity (DC) and Reverse Polarity (AC). Straight Polarity is the most common type of polarity, and it’s what most welders use. Reverse Polarity is less common but it can be used in some cases.
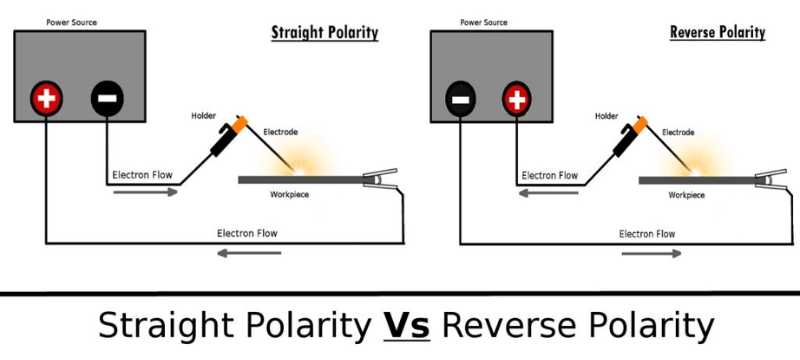
The type of metal you’re welding will dictate which type of polarity you need to use. For example, most steels can be welded with either DC or AC, but aluminum must be welded with AC.
To change the polarity on a MIG welder, all you need to do is switch the leads. The positive lead goes to the anode (red), and the negative lead goes to the cathode (black).
It’s important to note that some MIG welders have a “polarity switch” that allows you to quickly and easily change the polarity. Others might not have this feature, so you’ll need to manually change the leads yourself.
Once you know which type of polarity to use, it’s time to start welding! Remember to practice safety at all times and always follow the manufacturer’s instructions.
How to set MIG welding polarity settings for best results?
The first step is to determine what type of polarity you will be using. As mentioned above, the most common type of polarity used in MIG welding is direct current (DC).
- Once you have determined the type of polarity you will be using, the next step is to set your welder to the correct settings.
- For DC welding, there are two types of electrode connections: positive (+) and negative (-).
- A positive electrode connection is typically used for welding thick metals. It produces a more powerful arc that penetrates the metal better.
- A negative electrode connection is typically used for welding thin metals. It produces a softer arc that is less likely to cause weld defects.
Now that you know how to set your MIG welder’s polarity settings for the best results, it’s time to get started on your next welding project!
Tips for troubleshooting when things go wrong
If your MIG welder is not producing the desired results, there are a few things you can do to troubleshoot the issue.
1) Correct polarity setting
First, check to make sure that the correct polarity setting is selected on your welder. If the wrong polarity is selected, it can cause weld defects.
2) Welding current
Another thing to check is the welding current. If the current is too high, it can cause the weld to be too hot and cause warping or other defects. Conversely, if the current is too low; the weld may not be hot enough and will not penetrate the metal properly.
3) Wire feed speed
The wire feed speed can also affect the quality of the weld. If the wire feed speed is too high, it can cause the weld to be overcooked. On the other hand, if the wire feed speed is too low; the weld may not have enough time to properly fuse the metals together.
4) Check the Gas flow rate
Next, check to see if the gas flow rate is set correctly. The gas flow rate should be set so that the gas surrounds the weld pool and protects it from oxygen and other contaminants.
5) Ask from Professionals
If you are still having difficulty achieving the desired results, consult your MIG welder’s manual or ask a professional for guidance.
MIG welding is a versatile and powerful welding process that can be used to weld a variety of different metals.
By following these tips, you can ensure that your next welding project is a success!
FAQs – MIG welding polarity
What is straight polarity?
Straight polarity is when the electrode is connected to the positive terminal of the welder and the workpiece is connected to the negative terminal. This configuration creates a more powerful arc that penetrates the metal better. It is typically used for welding thick metals.
What polarity should MIG welding be set at?
MIG welding should be set at the correct polarity for the specific project. For most projects, direct current (DC) is used. However, alternating current (AC) can be used for some applications.
How do you change the polarity on a MIG welder?
In order to change the polarity on a MIG welder, you will need to first turn off the power to the machine. Next, you will need to remove the wire feed assembly from the welder.
Once the wire feed assembly is removed, you will be able to access the polarity switch. Simply flip the switch to the desired setting and then reassemble the welder.
Do you push or pull MIG welding?
MIG welding can be done with either a push or pull motion. The push motion is when the electrode is pushed away from the welder and the pull motion is when the electrode is pulled toward the welder.
What polarity do you use for solid wire?
For solid wire, the most common type of polarity used is direct current (DC). DC can be either positive or negative. If you are unsure of which electrode connection to use, consult your MIG welder’s manual or ask a professional for guidance.
Wrap Up
Setting your MIG welding polarity is an important step in the welding process. If you set it up incorrectly, you could end up with a weld that isn’t strong enough or has too much splatter.
Setting your polarity is an important step in welding. You need to make sure that the current is flowing in the correct direction so that you create a good weld.
In general, setting your polarity to negative will produce better welds on thin metals while positive polarity is better for thicker metals. If in doubt, start with a negative setting and adjust as needed.
We hope this article has helped to clear up any confusion about how to set your MIG welding polarity and that you are now ready to start welding like a pro!




